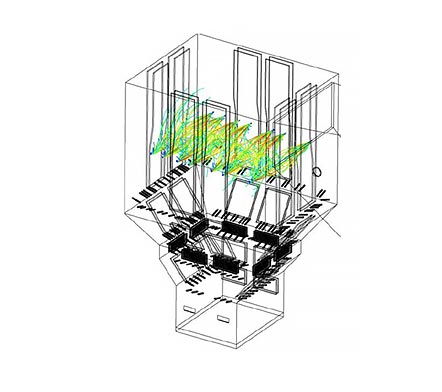
SNCR systems provide a low-cost technique to reduce NOx emissions by 30%–75% for boilers, furnaces and kilns.
The SNCR process involves injecting a reagent into the flue gas in the appropriate temperature window. The reagent reacts with NOx to form harmless nitrogen and water. The design, arrangement, and location of the reagent injectors are critical to the performance of the SNCR system. Our advanced technology utilizes variable droplet size control and automatic tilting injectors based on furnace temperature, to enhance the NOx reduction performance.
SNCR System Package
Our SNCR systems include reagent storage tanks, pumping and flow control, reagent injection systems, and a boiler control interface. CCA also provides experienced field engineers for optimizing the SNCR in conjunction with the combustion system and overall operations.
Features & Benefits
- Injection of urea or ammonia (mixed with air and water) into furnace section of field erected boilers
- NOx reduction reaction temperature window: 1,650–2,100 °F
- Optimum injector locations determined by CFD modeling of furnace and exhaust gas profiles
- CCA developed unique tilting injector design to improve efficiency and reduce equipment costs
- Low total cost of ownership
- High-efficiency NOx removal, providing 30%–75% reduction
- Energy efficient
- Easy to retrofit with minimal downtime


Dallas, TX, USA
Phone: 833-4NOxSCR (833-466-9727)
Monroe, CT, USA
Phone: 203-268-3139
Stansted, Essex, United Kingdom
Phone: +44-1439-330623
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Phone: +971 (0) 4434 0004
Singapore
Phone: +65-6472-0020
Shanghai, China
Phone: +86-21-62560387